Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Management, and Medication Options
When your body stops responding properly to insulin, you’re dealing with type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition where blood sugar stays too high because the body doesn’t use insulin the way it should. Also known as insulin resistance, it’s not just about eating too much sugar—it’s about how your cells react, or don’t react, to the hormone that moves glucose into your muscles and organs. Unlike type 1, where the body doesn’t make insulin at all, type 2 diabetes means your body still makes it, but it’s like the lock on the door is rusted—insulin knocks, but the cells won’t open up.
This condition doesn’t happen overnight. It builds over years, often starting with prediabetes, where blood sugar is higher than normal but not yet in the diabetic range. Many people don’t know they have it until they feel tired all the time, get thirsty constantly, or notice slow-healing cuts. It’s closely tied to weight, especially belly fat, but not everyone with type 2 diabetes is overweight. Genetics, lack of movement, and even stress can play a role. insulin resistance, the core problem behind type 2 diabetes is what drives the need for medication. And when diet and exercise aren’t enough, drugs like metformin, the most common first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes come in. Others, like saxagliptin (Onglyza) and repaglinide (Prandin), work differently—some boost insulin release, others help your body use insulin better, and a few even slow down how fast your liver dumps sugar into your blood. These aren’t just pills you take—they’re tools that fit into a bigger picture of daily habits, monitoring, and long-term health.
Managing type 2 diabetes isn’t about perfection. It’s about consistency. Small changes—walking after dinner, swapping soda for water, checking your blood sugar a few times a week—add up. The goal isn’t to eliminate sugar forever, but to keep your levels steady so you don’t end up with nerve damage, kidney issues, or heart problems down the road. You’ll find real comparisons here between drugs like Onglyza and repaglinide, how they stack up against each other, what side effects to watch for, and which ones might work better for your lifestyle. There’s also info on how weight, diet, and other conditions like high blood pressure or gout tie into the picture. This isn’t theory. It’s what people are actually using, what works, and what doesn’t—straight from real-world experience.
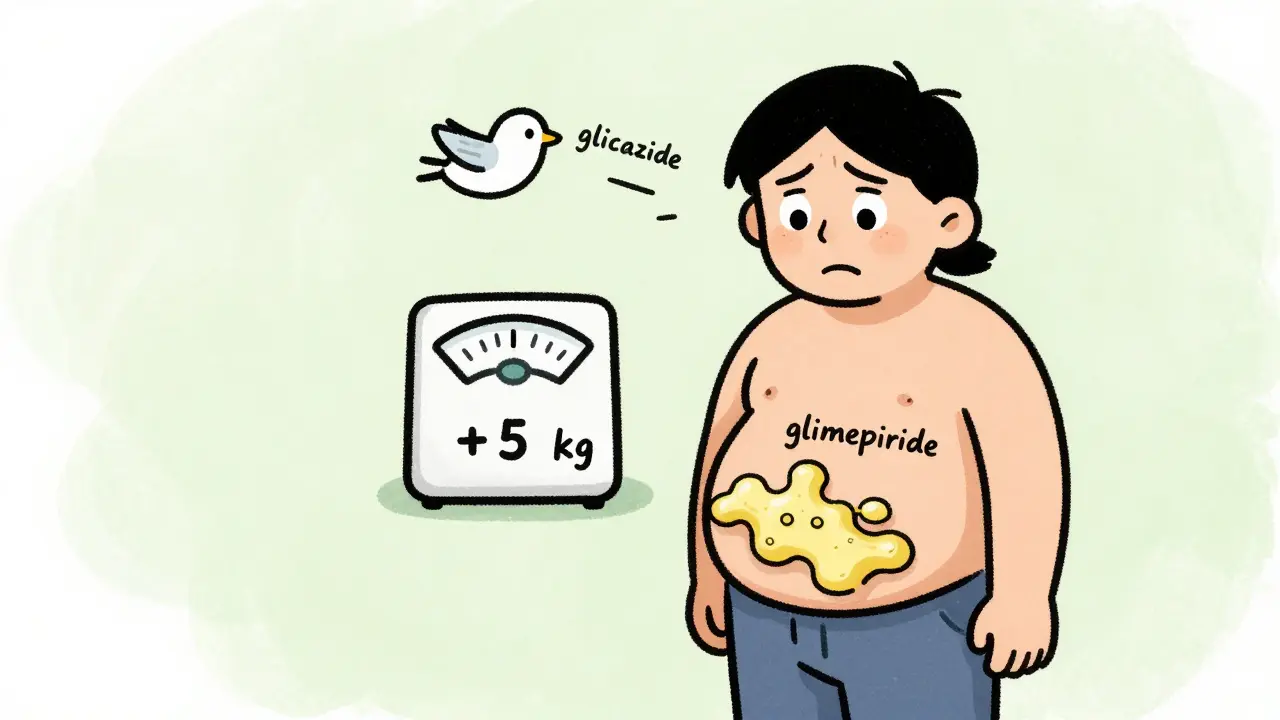
Sulfonylureas and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know Long-Term
Sulfonylureas help control blood sugar but often cause weight gain, making diabetes harder to manage long-term. Learn which drugs cause the most gain, how to fight it, and what alternatives exist.
Keep ReadingCompare Actos (Pioglitazone) with Alternatives for Type 2 Diabetes
Compare Actos (pioglitazone) with modern diabetes alternatives like metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 agonists. Learn which options are safer, more effective, and better for heart and kidney health.
Keep Reading