Cyclosporine: Practical Guide to Uses, Risks and Safe Use
Cyclosporine is a strong immunosuppressant used to prevent organ rejection and treat certain autoimmune conditions. It works by blocking calcineurin, which lowers the activity of T cells that drive immune attacks. That power helps when the immune system is doing harm, but it also means cyclosporine needs careful handling and monitoring.
How cyclosporine works & common uses
Doctors prescribe cyclosporine for kidney, liver, and heart transplant patients to stop rejection. It's also used for severe rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and hard-to-treat atopic dermatitis or uveitis. Formulations include oral capsules, oral solution, and intravenous dosing in hospitals. Typical maintenance dosing for oral cyclosporine is roughly 2.5–5 mg/kg per day split into two doses, but your doctor will tailor the amount and track blood levels to keep it safe and effective.
Side effects, monitoring and safe use
Common side effects include high blood pressure, kidney problems, tremor, excess hair growth, and swollen gums. Serious risks are infections and kidney damage. Because of this, clinicians check creatinine, electrolytes, blood pressure, and drug levels regularly, especially in the first weeks. Cyclosporine interacts with many medicines: avoid grapefruit and tell your doctor about antibiotics like erythromycin, antifungals such as ketoconazole, and common drugs that change metabolism. Those interactions can raise cyclosporine levels and increase toxicity.
Do not stop cyclosporine suddenly without medical advice; that can trigger disease flare or rejection. Women who are pregnant or planning pregnancy should discuss alternatives; cyclosporine can be used in pregnancy sometimes, but risks and benefits must be weighed. Breastfeeding while on cyclosporine needs a specialist's input because small amounts pass into breast milk.
Practical tips: take doses at the same times each day, stick to the prescribed formulation, and keep a list of all medicines and supplements. Drink enough water but avoid large amounts of grapefruit or grapefruit juice. Report fever, sore throat, reduced urine, or new swelling to your care team right away. If you take other drugs that change liver enzymes, your provider may change your cyclosporine dose or monitor levels more often.
Quick checklist for patients: bring a current medication list to every visit, get creatinine and blood pressure checked at least every 1–2 weeks when starting or changing dose, then monthly once stable. Ask your team about trough drug levels (often called C0 or C2) after dose changes. Avoid live vaccines while on treatment and use sun protection, immunosuppression can raise infection and skin cancer risk. Keep an emergency contact for sudden fevers or shrinking urine output.
Buying cyclosporine: always use a licensed pharmacy and a valid prescription. Online sellers that offer prescription drugs without a prescription are risky, avoid them. If cost is an issue, ask your prescriber about generic options, manufacturer savings programs, or patient assistance resources. Pharmacists can also help clarify dosing and interactions.
Keep this in mind: cyclosporine can be essential for transplants and some autoimmune conditions, but it needs regular lab checks, attention to drug interactions, and honest communication with your medical team. Follow monitoring schedules, report side effects quickly, and use reputable pharmacies to keep treatment safe and effective.
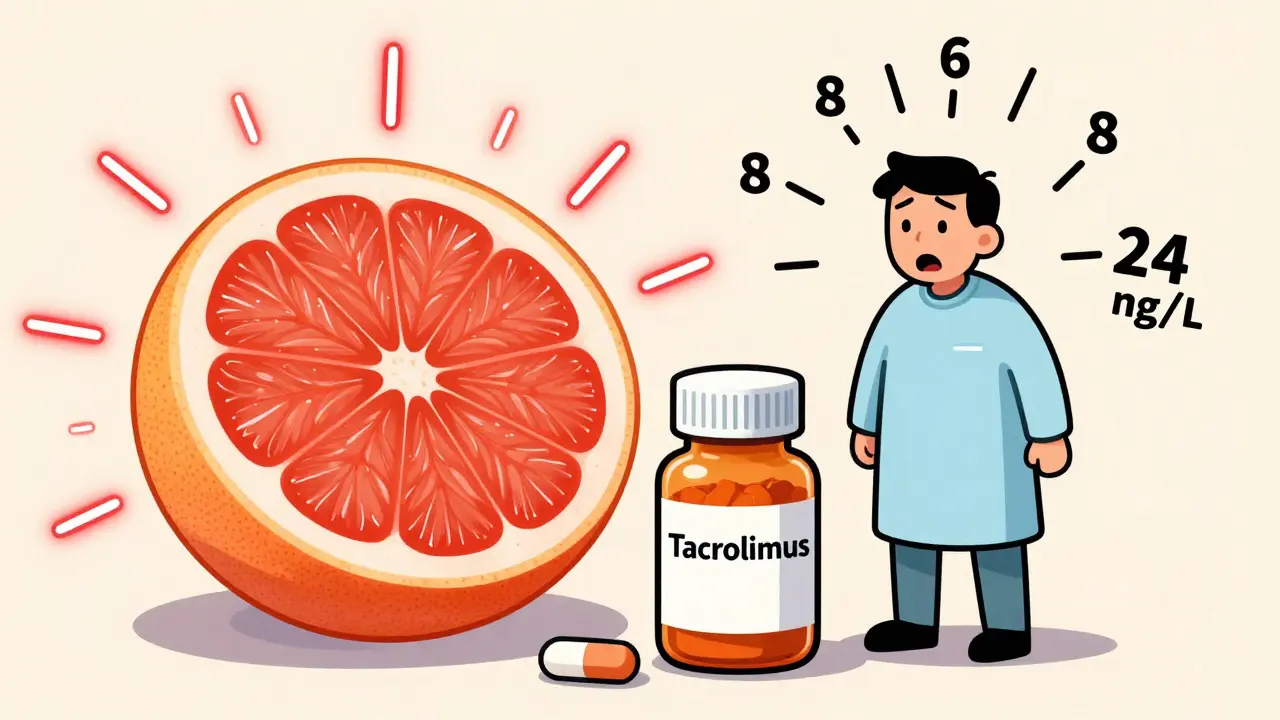
Grapefruit and Immunosuppressants: What You Need to Know Before Eating One
Grapefruit can dangerously increase levels of immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and tacrolimus, raising the risk of kidney damage and infections. Even small amounts can cause toxic effects that last up to 72 hours. Avoid all grapefruit products if you're on these medications.
Keep ReadingCyclosporine and the Heart: A Comprehensive Guide
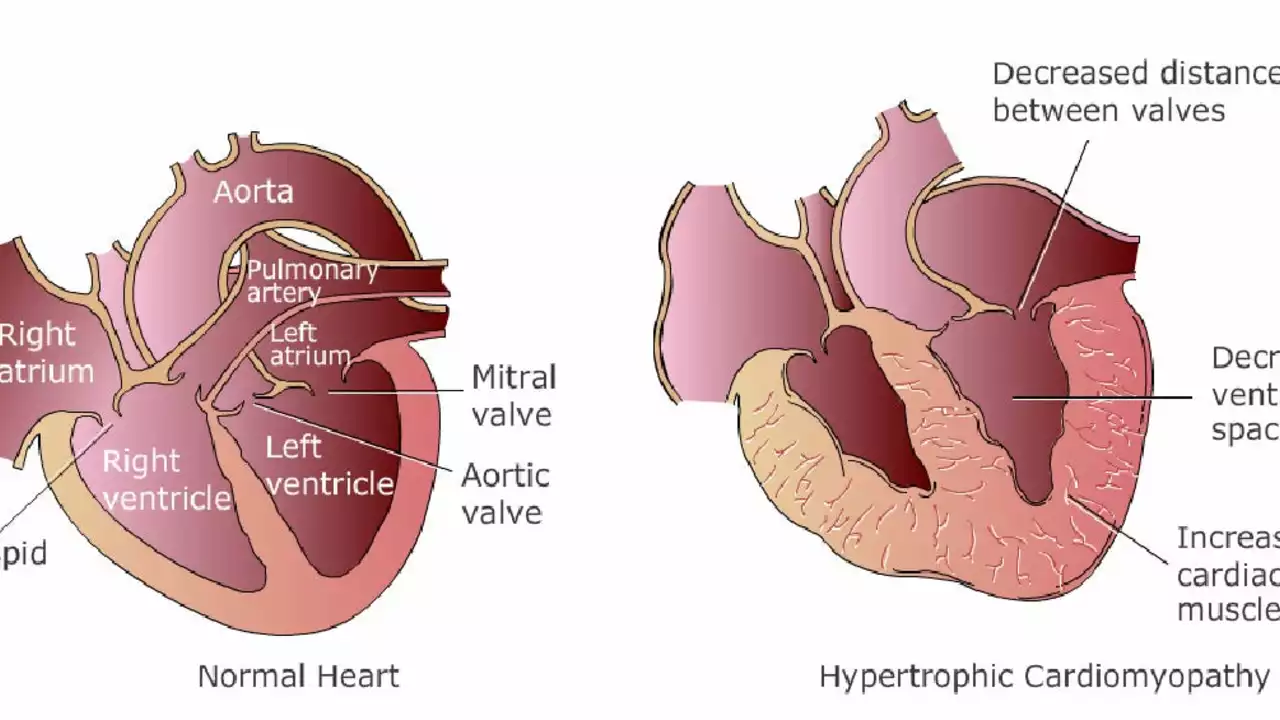
Cyclosporine is a powerful immunosuppressant drug that has significantly improved the success rates of organ transplant surgeries, including heart transplants. It works by suppressing the body's immune system, preventing it from attacking the newly transplanted organ. However, like with any medication, there are potential side effects and risks associated with its use. Some studies have shown that cyclosporine can cause high blood pressure and kidney damage, which can, in turn, negatively affect the heart. As a result, it's crucial for doctors and patients to carefully monitor and manage these potential side effects to ensure the best possible outcomes for heart transplant recipients.
Keep ReadingCyclosporine and the Heart: A Comprehensive Guide
As a blogger, I recently came across a comprehensive guide on Cyclosporine and its impact on the heart. Cyclosporine, an immunosuppressive drug, is commonly used to prevent organ rejection after transplantation surgeries. However, it's crucial to be aware of its potential side effects, particularly on the heart. The guide discussed topics like hypertension, cardiotoxicity, and the importance of regular monitoring for those taking Cyclosporine. I highly recommend checking out this guide to better understand the implications of this medication on heart health.
Keep Reading