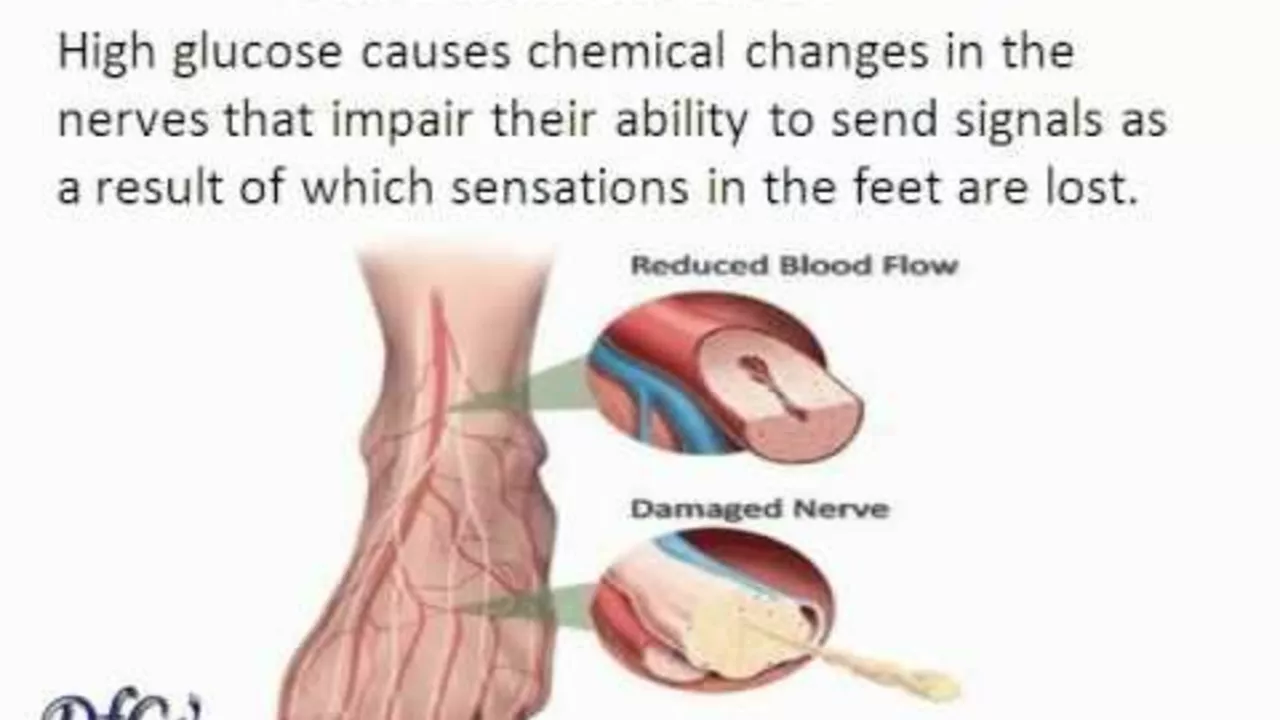
Understanding Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar levels can injure nerves throughout your body, but DPN primarily affects nerves in your legs and feet. It's a common complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Symptoms include numbness, pain, and weakness in the feet and legs. It's important to understand the condition in order to manage it properly.
Identifying the Symptoms of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Early detection of DPN begins with recognizing the symptoms. These can range from numbness, tingling, or pain in the toes to severe pain that interferes with your sleep. You may also experience muscle weakness and loss of reflexes, especially at the ankle. Identifying these symptoms early on can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of DPN is crucial because it allows for early intervention. This can help slow the progression of the disease, alleviate pain, and reduce the risk of further complications, such as foot ulcers, infections, and amputations. Delaying diagnosis and treatment can result in irreversible nerve damage.
Risks of Delayed Detection and Treatment
If left untreated, DPN can lead to serious complications. These can include infections and ulcers in the feet, which can be difficult to treat and could lead to amputation. Additionally, the loss of sensation in the feet can make it difficult to notice injuries, leading to further complications.
Diagnosing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diagnosis of DPN involves a thorough physical examination, including neurological tests to assess your sensory perception and reflexes. Your doctor may also conduct a nerve conduction study or electromyography to assess the severity of the nerve damage.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Treatment for DPN focuses on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. This can involve medication for pain relief, physical therapy to improve mobility, and strategies to manage underlying conditions like diabetes. Regular foot care is also crucial to prevent complications.
Preventing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
While DPN is a common complication of diabetes, it's not inevitable. Good blood sugar control can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and regular check-ups can also help prevent DPN.
Living with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Living with DPN can be challenging, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage your symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. This involves regular foot care, wearing appropriate footwear, and monitoring your blood sugar levels consistently.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness and Action
In conclusion, early detection and treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy is crucial to managing this condition and preventing serious complications. By staying aware of the symptoms, getting regular check-ups, and managing your diabetes, you can protect your nerve health and maintain your quality of life.






17 Comments
Wow, you really think you can brush off diabetic peripheral neuropathy like it’s just another foot ache? Let me set the record straight before you start spreading sunshine. Early detection isn’t a nice-to-have, it’s the lifeline that decides whether you’ll be hobbling in shoes or fighting off a nasty amputation. The numbness you dismiss today can morph into a burning agony that sleeps on your bed, stealing your rest and your sanity. Sugar spikes don’t just mess with your pancreas; they chew up the delicate fibers of your nerves like termites on a wooden fence. If you ignore the tingling, you’re basically signing a contract with pain that you’ll pay for later. Studies show that patients who get evaluated within six months of symptom onset have a 40% lower chance of developing foot ulcers. That’s not a statistic, that’s a warning shouted across a hospital hallway. The “just a little tingling” excuse is the same lie the insurance companies love to hear. Your doctor can run a simple monofilament test, and within minutes you’ll know if your foot is a ticking time bomb. Don’t be the person who waits until a blister becomes gangrene before you finally see a podiatrist. Those swollen corners of the foot aren’t just ugly-they’re harbingers of infection, and infection can spread faster than gossip in a small town. And when you finally get to the operating room, the odds of a clean recovery drop dramatically because the nerves have already gone soft. So stop playing the victim and start playing the proactive patient. Put your glucose numbers under a microscope, schedule that nerve conduction study, and give your feet the attention they deserve. Your future self will thank you, unless you decide you’d rather be the cautionary tale on a health forum.
Listen up, buddy, if you’re sitting there thinking your toes can just “feel fine” tomorrow, you’re kidding yourself. A dash of creative language won’t hide the fact that those pins‑and‑needles are screaming for help. Slip on a pair of snug shoes, ignore the poke, and you’ll be dancing on broken bones in no time.
While the prevailing consensus extols early screening, one must consider that not every patient benefits equally from aggressive testing. The literature, albeit abundant, often overlooks the cost‑benefit ratio in low‑risk cohorts. It is prudent to tailor diagnostic protocols rather than adopt a blanket approach.
Hey, Ellie, I hear you loud and clear! Let’s channel that fire into something positive – keep checking those feet daily and grab a doc if anything feels off. You’ve got this, and we’re all rooting for you!
👍 Totally agree, Juan! Regular foot checks are a game‑changer. 😊 Don't forget to moisturize to avoid cracks.
The so‑called “cost‑benefit” argument often ignores the human cost of delayed diagnosis. When a patient’s foot ulcer spirals into infection, the price is measured in pain, not spreadsheets. Ethical practice demands we err on the side of prevention.
Indeed, Liliana, the ethical dimension you raise resonates profoundly with the broader discourse on chronic disease management. When we dissect the layers of patient outcomes, we encounter a tapestry woven from early intervention, sustained glycemic control, interdisciplinary collaboration, and patient education. Each thread, if neglected, unravels the integrity of the whole system, precipitating a cascade of complications that could have been mitigated. Therefore, a proactive stance-anchored in evidence‑based screening protocols-serves not merely as a clinical recommendation but as a moral imperative that safeguards both individual well‑being and societal health resources.
Boom! Early detection is the secret sauce, and you just nailed it! Let’s keep those feet happy and healthy!
Absolutely, Sadie. By integrating daily foot inspections with balanced blood sugar management, patients can dramatically reduce the risk of nerve damage. It’s a straightforward routine that yields big rewards.
While the sentiment expressed is commendable, it must be underscored that such recommendations are insufficient without rigorous clinical validation. Empirical data, preferably from randomized controlled trials, should substantiate any prophylactic regimen before it is promulgated as standard practice.
The advice to moisturize sounds nice, but it skirts the deeper issue of neuropathic pain management, which remains under‑addressed in most lay discussions.
Sounds fine.
One must question the superficiality of such a terse affirmation, for it betrays a lack of engagement with the profound implications of diabetic neuropathy management.
Indeed, Theunis, the gravity of the situation demands more than hollow platitudes; it calls for decisive action, comprehensive screening, and unwavering commitment to patient education.
Leveraging a multidisciplinary approach-incorporating podiatric assessments, neurophysiological diagnostics, and glycemic optimization algorithms-facilitates a robust therapeutic framework that mitigates neuropathic sequelae.
That’s spot on, Andrew. A clear plan with regular EMG checks and proper footwear can really keep things in check.
i think its work.